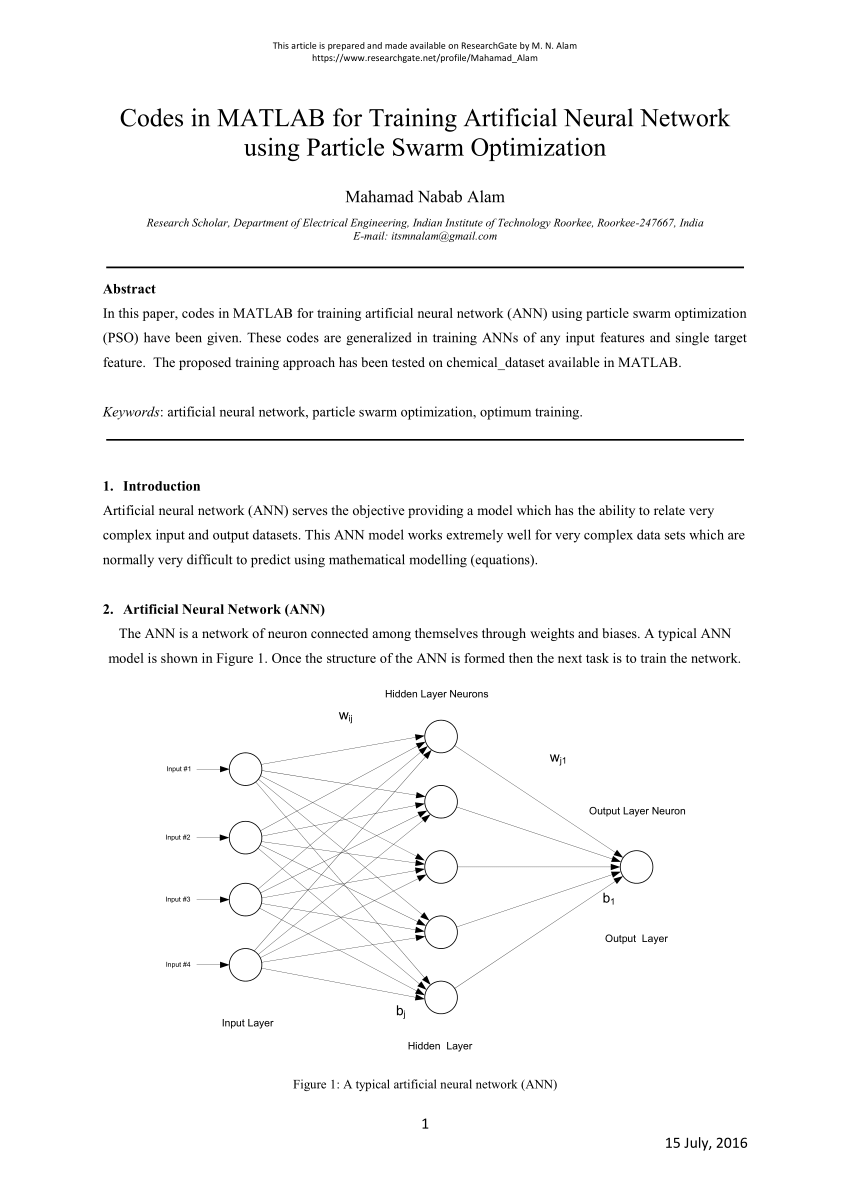
Download FREE PDF Mathematics Ebooks for IIT JEE Main and JEE Advance and All other Engineering exams. IIT Books is free site for JEE Main & Advance Preparation.IIT Books give Free Study material papers and latest news of all engineering entrance exam. Wave Optics Class Notes PDF For IIT JEE Here we are providing Allen institute wave optics class notes pdf for JEE Main 2018 exam. https://lanegol.netlify.app/iit-jee-books-pdf.html.
- Compiler Design Tutorial
- Compiler Design Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
Optimization is a program transformation technique, which tries to improve the code by making it consume less resources (i.e. CPU, Memory) and deliver high speed.
In optimization, high-level general programming constructs are replaced by very efficient low-level programming codes. A code optimizing process must follow the three rules given below:
Bach formatted in Encore, ready to use. New Features Gvox VSTi Host Toolbar now displays all tools Preroll click option New Score Wizard Over 30 Templates and unlimited user created template Transposed or 'C' score option. Encore 5 full crack free download. Beginning measure number offset Preset Tab tunings option Added menu items Auto Spacing when dragging notes, barlines and systems Enhanced MIDI playback Garritan Personal Studio ready Simplified Accidentals option More shortcuts MusicXML import and export Full DLS and Soundfont support Handwritten Music Style option Bonus - Hundreds of works by J.S. Top 4 Download periodically updates software information of Encore 5.0.4 B858 full version from the publisher, but some information may be slightly out-of-date.
The output code must not, in any way, change the meaning of the program.
Optimization should increase the speed of the program and if possible, the program should demand less number of resources.
Optimization should itself be fast and should not delay the overall compiling process.
Efforts for an optimized code can be made at various levels of compiling the process.
At the beginning, users can change/rearrange the code or use better algorithms to write the code.
After generating intermediate code, the compiler can modify the intermediate code by address calculations and improving loops.
While producing the target machine code, the compiler can make use of memory hierarchy and CPU registers.
Optimization can be categorized broadly into two types : machine independent and machine dependent.
Machine-independent Optimization

In this optimization, the compiler takes in the intermediate code and transforms a part of the code that does not involve any CPU registers and/or absolute memory locations. For example:
This code involves repeated assignment of the identifier item, which if we put this way:
should not only save the CPU cycles, but can be used on any processor.
Machine-dependent Optimization
Machine-dependent optimization is done after the target code has been generated and when the code is transformed according to the target machine architecture. It involves CPU registers and may have absolute memory references rather than relative references. Machine-dependent optimizers put efforts to take maximum advantage of memory hierarchy.
Basic Blocks
Source codes generally have a number of instructions, which are always executed in sequence and are considered as the basic blocks of the code. These basic blocks do not have any jump statements among them, i.e., when the first instruction is executed, all the instructions in the same basic block will be executed in their sequence of appearance without losing the flow control of the program.
A program can have various constructs as basic blocks, like IF-THEN-ELSE, SWITCH-CASE conditional statements and loops such as DO-WHILE, FOR, and REPEAT-UNTIL, etc.
Basic block identification
We may use the following algorithm to find the basic blocks in a program:
Search header statements of all the basic blocks from where a basic block starts:
- First statement of a program.
- Statements that are target of any branch (conditional/unconditional).
- Statements that follow any branch statement.
Header statements and the statements following them form a basic block.
A basic block does not include any header statement of any other basic block.
Basic blocks are important concepts from both code generation and optimization point of view.
Basic blocks play an important role in identifying variables, which are being used more than once in a single basic block. If any variable is being used more than once, the register memory allocated to that variable need not be emptied unless the block finishes execution.
Control Flow Graph
C Code Optimization
Basic blocks in a program can be represented by means of control flow graphs. A control flow graph depicts how the program control is being passed among the blocks. It is a useful tool that helps in optimization by help locating any unwanted loops in the program.
Loop Optimization
Most programs run as a loop in the system. It becomes necessary to optimize the loops in order to save CPU cycles and memory. Loops can be optimized by the following techniques:
Invariant code : A fragment of code that resides in the loop and computes the same value at each iteration is called a loop-invariant code. This code can be moved out of the loop by saving it to be computed only once, rather than with each iteration.
Induction analysis : A variable is called an induction variable if its value is altered within the loop by a loop-invariant value.
Strength reduction : There are expressions that consume more CPU cycles, time, and memory. These expressions should be replaced with cheaper expressions without compromising the output of expression. For example, multiplication (x * 2) is expensive in terms of CPU cycles than (x << 1) and yields the same result.
Dead-code Elimination
Dead code is one or more than one code statements, which are:
Code Optimization Techniques
- Either never executed or unreachable,
- Or if executed, their output is never used.
Thus, dead code plays no role in any program operation and therefore it can simply be eliminated.
Code Optimization Definition
Partially dead code
There are some code statements whose computed values are used only under certain circumstances, i.e., sometimes the values are used and sometimes they are not. Such codes are known as partially dead-code.
The above control flow graph depicts a chunk of program where variable ‘a’ is used to assign the output of expression ‘x * y’. Let us assume that the value assigned to ‘a’ is never used inside the loop.Immediately after the control leaves the loop, ‘a’ is assigned the value of variable ‘z’, which would be used later in the program. We conclude here that the assignment code of ‘a’ is never used anywhere, therefore it is eligible to be eliminated.
Likewise, the picture above depicts that the conditional statement is always false, implying that the code, written in true case, will never be executed, hence it can be removed.
Partial Redundancy
Redundant expressions are computed more than once in parallel path, without any change in operands.whereas partial-redundant expressions are computed more than once in a path, without any change in operands. For example,
C Code Optimization Techniques Pdf Download
[redundant expression] | [partially redundant expression] |
Loop-invariant code is partially redundant and can be eliminated by using a code-motion technique.
Software Optimization Techniques
Another example of a partially redundant code can be:
C Code Optimization Techniques Pdf Online
We assume that the values of operands (y and z) are not changed from assignment of variable a to variable c. Here, if the condition statement is true, then y OP z is computed twice, otherwise once. Code motion can be used to eliminate this redundancy, as shown below:
Here, whether the condition is true or false; y OP z should be computed only once.